Menu
Table of contents
Optimizing for the search engines (read: Google) can be done outside your own website, such as through link building. Think guest blogging, distributing infographics or social media links.
But optimization can then also be done within your website. Think about optimizing the technology or improving your content.
Yet there is another division we can make within SEO. Namely, between off page SEO and on page SEO. And about the latter, that's what I'm going to talk about today.
Ps. We also recorded a podcast on this topic. You can find that on Spotify, as well as on YouTube:
What is on-page SEO?
On page SEO is the optimization of various components within a page to ensure that the page ranks as well as possible for a predetermined keyword.
In other words, On page SEO is adjusting a page's technique, content and authority to rank #1. Because ultimately, that's the goal. The famous No. 1 position.
I want to take a little jump back. Because if you didn't already know: SEO consists of three parts:
1. Technology (speed, mobile display, sitemap, etc.)
2. Content (Text, images and video).
3. Authority (Internal links, external links, etc.)
Do pay close attention to the numbers I noted above. Because you ALWAYS start with the technical optimization of a website, then you tackle the content and lastly you start working on authority.
Think of website technology as the foundation of a house. Without a good foundation, you can't start building.
The same applies to websites. Content then can be thought of as the walls of a house, giving the house (and thus your Web site) volume and allowing the foundation to come into its own. To complete the house, you also need a roof, which in this case is the authority.
Who completes your website and makes sure the technology and content are used to their ultimate potential.
Difference between on page and off page SEO
So how does on-page differ from off-page SEO? The name says it all: off-page SEO, unlike on-page, is all about factors that cannot be found directly on your page or even website.
That is, with off page SEO, you need other websites to positively influence your rankings. You do that primarily by link building.
By ensuring that other websites link to your website or specific page. You can do this by promoting your content on social media or through other blogs, but you often have no guarantee that the content will be shared or generate actual backlinks.
In short, it is usually more difficult to optimize for off page factors than for on page elements, which you can influence yourself. Therefore, let's zoom in further on the latter.
What elements fall under on page SEO?
Before I start talking about the elements that fall under on page SEO, it is also important to mention that certain elements do not belong so much to on page SEO, but more to SEO in general. At least in my opinion.
For example, by improving the load time of one specific page you affect the ranking potential of that page, but it also does something for your website as a whole. True, maybe not a whole lot, but still.
Every little bit helps. Also consider the sitemap, the 404 page or AMP, for example.
Elements that you can control and that influence the rankings of one page, but also of your website as a whole. And so there are more elements that I think do not necessarily belong to on page SEO (but opinions differ about that).
In this article, therefore, I'm going to talk purely about some of the factors you can influence that literally fall within one page.
And those factors are:
- URL
- H1 (Title)
- H2
- Outbound internal links
- Outbound external links
- Loading speed
- Structured data
- Images (name and alt text)
- Meta title
- Meta description
- Action (buttons)
- Semantics
- Text (Yoast / Rank Math plugin, word count, etc.)
Now I am going to explain what is so important about each part. Let's move on quickly.

URL
The URL is what you type in on to get to a Web site. For example: https://onlinemarketingagency.com/online-marketing-bureau-arnhem.
What is incredibly important about the URL is that you incorporate the keyword you have chosen for that page into the URL. In the example above that is: 'online marketing agency arnhem'.
It is also important to keep the URL as short and as clean as possible. So that's the rule of thumb I use: always as short as possible and no unnecessary characters like a ?, a _ or numbers.
So don't go for https://onlinemarketingagency.com/locaties/arnhem/online-marketing-seo-sea-social-media-website-webshops?-facebook_instagram_twitter/.
H1 (Title)
The H1 is often the title of a page or article and with it you indicate the main textual content of the page. Often the H1 is one word to a whole sentence long.
In this article, the title at the top is the H1. With the H1, it is also a must that you use the keyword, as this is one of the most important parts that Google looks at with regard to determining the topic of your web page.
The rule that is important here is that every page should have an H1, but also should not have more than one. Also, always make sure the H1 excites, persuades and covers the page's content well enough.
H2 (Intermediate headings)
The H2 is often used for the headings and in it you incorporate the second most important textual content. The headings are important because texts often stop being read in full and they make the text scannable.
So people scan through the text looking for interesting and relevant pieces of content, paying particular attention to the headings That the headings should excite, invite and cover the load is therefore self-evident.
The rule of thumb that is important with the H2 is that each page should have at least one H2. More H2s per page are allowed and I definitely recommend it.
Also, incorporate the search term sporadically in the H2s and play with semantic keywords in the H2s (but more on that later).
Outgoing links
A link within your Web site that links to another Web site is an outbound link. Outbound links are fine for several parties.
First of all, it is nice for the visitor, if you link to relevant content then you are helping the visitor along the way. By doing so, you are implicitly indicating that you want to help the visitor the best you can, and in doing so, you are not afraid to send people off your own website.
And that's what Google also wants, to help the visitor as much as possible.
Moreover, this also allows Google to see that the content of the outbound link is relevant, giving it an even better idea of exactly what your content is about. This allows Google to better place your content and perhaps better value it!
The rule of thumb I have here: link 1-2 times per article to an external websites and only link to websites that add value and do not contain crap.
Internal links
I see internal linking as a kind of hidden treasure. It's something very little is done, but which works very well.
For example, did you know that I went from spot 15/16 to spot 5 with some search terms by placing a few internal links?
Google should think of you as a visitor visiting your website. If a visitor can't find a page because the page is so verbose, Google is never going to let the page rank well.
So always link to potentially other relevant content on other pages on your website as well. If you've been paying attention then you've seen that I've done the same in this article.
Haven't you noticed? Then here's another example: All about the content calendar.
When it comes to internal linking, there are also some "rules" that are important:
- Link to relevant content, linking for the sake of linking is pointless.
- Link per article 2-5 times internally
- TIP: Don't just link when you've written a new article, boost pages by linking to the new page with old pages.
Loading speed
But Daniel, you just said: Loading speed does not fall under on page SEO, but under SEO generally. True.
Partly then.
Because things like images, GIFs, videos and other forms of content can indeed be properly optimized within one specific page. For example, in a previous blog I talked about how to optimize images so that your load time of that page is improved.
But you can also optimize videos. Did you upload the video to the website and then put it on the website?
Then put it on YouTube and make sure the video loads correctly. Saves a lot of loading time and a lot of MBs for your website visitor.
Want to know how fast your website is and what are the improvements in speed? I wrote a blog about that too, namely: 9 tools to test the speed of your website.
Structured data
Yes, I have written many blogs. And yes, I have also written a blog about structured data before.
You can find those here.
For that reason, I'm not going to explain structured data in full detail, but in short, it's marking up content to make it clear to Google what the content is about. Think: location, phone number, a recipe, reviews, products, review or an event, for example.
But then why is structured data beneficial to your on-page SEO? Because structured data helps the visitor get started and because it makes the content of your website more insightful/clearer for Google.
So a win-win situation.
The rule of thumb that's important here: your company's contact information should be highlighted, and that you should always look for things like reviews to be highlighted as well.
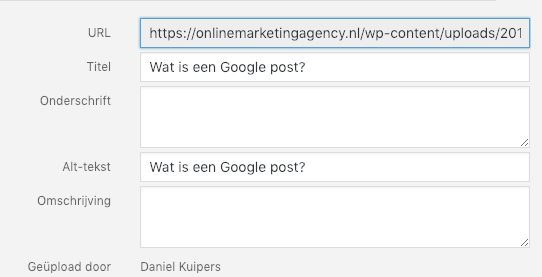
Title and alt text of images
I caught you at something! In fact, you have also sometimes uploaded an image with the name: screenshot-9123912.jpg or some other standard name.
Don't do it again.
Google is getting smarter, and these are also elements that Google looks/can look at. Just very black and white, but suppose you have a website and you always share the images from another website.
As a visitor and Google being what do you think of this? There is no right or wrong here, but the rule of thumb I use is always make the naming of an image specific.
For example, incorporate the search term in the name of your image or tell what the image is about. You should also do this with the alt text of an image.
Fill. Those. Always. In.
Always.
This is because the alt text is the text that is displayed if the image does not load for any reason. Thus, it indicates what the image is about, so that the visitors do not have to miss anything if it does not load.
Therefore, the alt text is direct Google requirement and one of the elements that Google considers important. Incorporate your search term into this as well.
Meta title
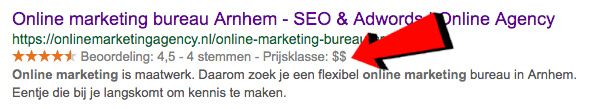
It still happens quite often, people who do not know exactly what the meta title is. Very simple: this is the title of the page that you will see in Google's search results.
Look!

With the meta title, you want to persuade Google users to click on your page. But how do you get people to click on your search result?
First of all, the meta title should match the visitor's search intent. So if someone googles on: 'have website made Arnhem'. Then someone wants a party that can create a website for him from Arnhem.
If you are from Amsterdam and have a landing page called "get website made Arnhem. Then that intention does not quite match what you are offering.
When coming up with a meta title, you need to make sure the title is inviting, thought-provoking, unique and stands out. The rule of thumb I have here: look at your competitors (the pages that already rank high on a particular search term) and come up with a better meta title that responds to the searcher's intent.
Then in Google Search Console, see how much it actually gets clicked and adjust the meta title if it doesn't work. And don't forget: incorporate your keyword here (extremely important!).
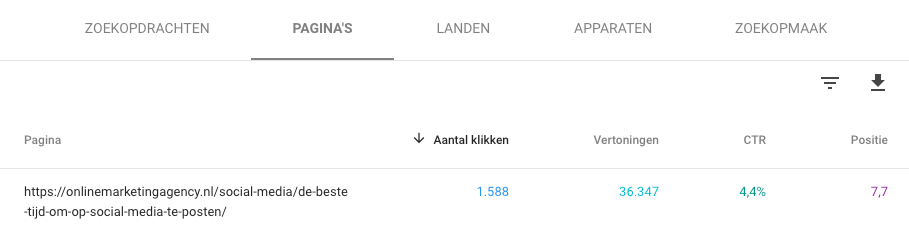
Meta description
The meta title by itself should make people click on your search result. However, people may want more information and will read the meta description.
The meta description must contain the keyword, and the same rules apply to the meta description as to the meta title. Just make sure that the description matches the content on the page and that it is tasty enough to encourage further reading.
Action (buttons)
Huh, action?
Yes, action!
When visitors visit a page from Google and then leave the page without performing a click, it is called a bounce. A high bounce rate is not necessarily a bad thing.
For example, the bounce rate of a blog is often somewhat higher than the bounce rate of, say, a regional plumber. This depends entirely on the action the visitor wants to take next.
Therefore, it is very important that you encourage action within a page. This can be a call-to-action button, a pop-up notification or other form.
Let me make it concrete for you. Suppose you click on the number one position on a particular keyword. You don't find what you want, go back and move to number two.
There you do find what you are looking for, you linger and you click through.
If only you do that, it's of no interest to Google. But if thousands of people do that, then that may signal to Google that that first page does not meet search intent.
In other words, prompting action is ultimately a form of on-page SEO.
Semantics
Semantics has to do with the fact that Google not only looks at the word you use, but also at other elements within your text. So it's not as simple as shoe and footwear.
These are words that are similar to each other. Rutger Steenbergen of SEO Zwolle describes it very nicely:
"With semantic, Google looks beyond keywords. Instead, Google looks at 'entities.' There are entities for people, things and places.
With Semantic Search, Google stores all the properties and descriptions of a word as an entity. As a result, a word like 'tree' becomes much more than 4 letters on a web page, it really takes on meaning."
So take this into account within your text. Don't just tell people that you perform a particular service.
Talk about why you perform the service, what it provides, how long you've been doing it, get clients talking, etc. etc. By talking/typing a lot about the topic, you give a page and its keyword more body.
More meaning as an entity.
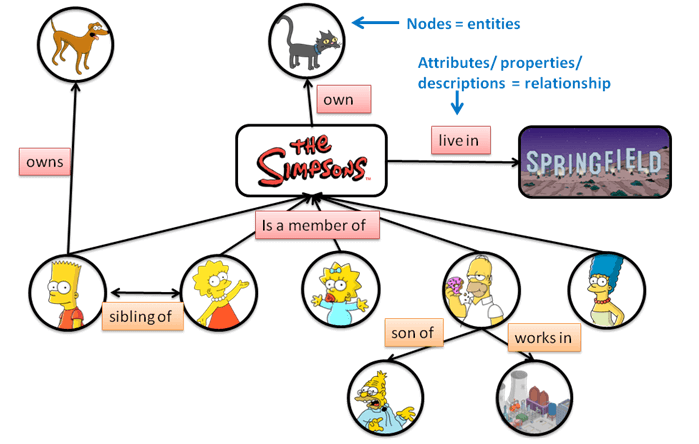
Bron: https://moz.com/blog/what-is-semantic-search
Text on a page
From semantics, we'll grab straight to the entire text on a page. My advice I have for you is: install the Rank Math or Yoast plugin if you own a WordPress website.
Why?
These plugins don't make you a terribly good copywriter right away or make your texts number one in no time. But they do give concrete tips and advice so you can make your text better, both in terms of SEO and readability.
For example:
- How often should the keyword be used?
- Should the keyword be used in the first and last paragraphs?
And I could go on and on. My advice is that you get your texts written by an experienced copywriter and work together to conquer Google.

These articles are must reads if you want to know more about on page SEO
Opinions differ, especially within the SEO landscape. Since I like to give you every possible resource so you can pop online, I've created a short list of blogs I read regularly that have been an inspiration for this article.
If you want to know more about SEO, you need to know these parties.
- https://moz.com/learn/seo/on-page-factors
- https://backlinko.com/on-page-seo
- https://neilpatel.com/blog/the-on-page-seo-cheat-sheet/
- https://www.semrush.com/blog/content-optimization-list-blogging-for-people-and-search-engines/
- https://ahrefs.com/blog/on-page-seo/
On page SEO software you need to know
Of course, you don't have to grab this little blog every time to check that you've applied all the on page SEO elements and haven't forgotten anything. You can, but you don't have to.
After all, there are easier ways to do that. Tools, software and handy extensions that control your page.
Tools like the Rank Math or Yoast plugin I told you about.
But there are more (and perhaps more comprehensive) on page SEO software programs out there. I list them for you:
SEMrush
This is currently my favorite from the list. Of all the SEO tools out there, SEMrush has by far the best and most comprehensive SEO audit. This feature within SEMrush is also called the Site Audit.
The Site Audit checks every page within your website for SEO. So it will look to see if all pages have an H1 or if a page's load time is long, etc.
In other words, SEMrush is great for figuring out all the on page SEO elements (and the areas of improvement within those elements).
Screaming Frog
And we continue with the second best on page SEO software out there: Screaming Frog.
When you first use Screaming Frog you think: uh, this seems like a very technical tool without any fancy formatting. And it may seem that way, but Screaming Frog is all about the content.
By simply entering a URL, you get a handy overview that lists all the on page SEO factors. And not only that.
Whereas the other tools are still about one URL, Screaming Frog gives you the elements of all the URLs within your website. That means you can retrieve all the elements of your entire website with a simple click of a button. And that's what makes Screaming Frog unique.
MozBar
The MozBar is a handy Chrome extension that lets you see at a glance the authority of specific pages and entire websites. But it also lets you see per page how all the on page SEO elements are completed, what the load time is, what the internal and external links are and so on.
So the whole list.
And to top it off, you can enter a search term and it will immediately give you some helpful tips and advice on how to further improve the page in question. You can download the MozBar here.
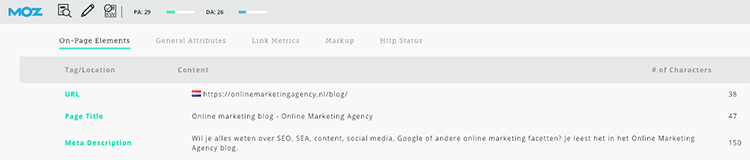
SEOSiteCheckup
SEOSiteCheckup analyzes your page on quite a few points. You can see not only if and how the meta-tags are filled in, how your (intermediate) headings are filled in, what your most common words are, what the loading speed is and you name it.
And should there be any problems, SEOSiteChekup immediately explains how to fix them.
Perhaps a bit overwhelming data, but no less useful. Small note: you can only do a limited number of analyses per day.
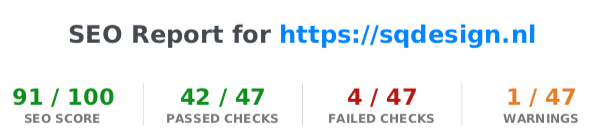
Sitechecker
There couldn't be a more obvious name for a tool that checks your website: Sitechecker. At Sitechecker.pro you can also request an extensive report validating your website on a huge number of points.
It is slightly less overwhelmingly designed than SEOSitesitecheckup and has convenient green, orange and red bullets so you can easily scroll through them to quickly discover pain points.
On-Page Optimization Tool from Internet Marketing Ninjas
Internet Marketing Ninjas' On-Page Optimization Tool has the great advantage that you can also enter your search term. It then indicates exactly how you used that search term.
How often you used it, for example. And what other words appear frequently in your text (see anyone there say anything about semantics?).
You can find the On-Page Optimization Tool here.
Neil Patel's SEO Analyzer
With this analysis tool from SEO guru Neil Patel, you can get insight into the words you use often (and whether they appear in your meta title, meta description and headings) and what the loading speed is like. Includes some handy advice for better on page SEO.
Moreover, you can not only check your page here, but you can also compare it with your competitors' pages. So if you implement the suggested improvements, you can immediately run another analysis to see if it has an effect compared to other pages that rank for the same search term.
Check out the SEO Analyzer here.
So, that's it again. Congratulations!
You slogged your way through this little blog.
Quite an achievement, but if all goes well, you now have the knowledge and software in place to set up your web pages in the best possible way for the search engines. And your visitors, not to mention your visitors.
If you have any questions or comments, you can reach me here. Or leave a comment below.
This article was written on February 4, 2019 and updated on September 17, 2023.
What is the purpose of on page SEO?
The goal of on page SEO is to optimize various elements within a web page, such as the technology, content and authority, to ensure that the page ranks high for a specific keyword.
What are important elements of on page SEO?
Important elements of on page SEO include URL structure, H1 and H2 headings, outbound and internal links, loading speed, use of structured data, naming and alt text of images, meta title and meta description, call-to-action buttons, semantics and the quality of text on the page.
What is the difference between on page and off page SEO?
On page SEO focuses on optimizing elements that are on the page, while off page SEO focuses on factors outside the page, such as getting backlinks from other websites.
What tools can be used for on page SEO analysis?
There are several tools for on page SEO analysis, including SEMrush, Screaming Frog, MozBar, SEOSiteCheckup, Sitechecker, Internet Marketing Ninjas' On-Page Optimization Tool, Neil Patel's SEO Analyzer, Rank Math and Yoast plugin for WordPress.












6 Responses to "On Page SEO: complete explanation to rank high in Google"
Super article this. I can't wait to start trying all the browser plugins. Thanks!
No thanks John. Good luck!
Very nicely written blog! I read that you should internally link 2-5 times per article, but you do this much more in this blog? So where exactly is the limit with how much you can internally link?
Thanks in advance,
Anne
Thanks for your compliment. The rule of thumb I use is 2-5 times per article. Of course, this depends on the length of the article.
In addition, you always link internally primarily for the visitor, not for Google. So should an internal link help the visitor further, of course you may always add more.
Hi Daniel, thanks for sharing this information. How do you deal with multiple synonyms of a keyword. You see, I sell final drives, travel motors and travel drives. Three different names for the same product. How do you best handle this?
Thanks and regards,
Jaap
Good question Jaap! I would just type them all into Google and see what you see. If you see the same results for all terms, then you know you need to combine them. Is that not the case? Then you can turn them into separate pages.