Menu
Table of contents
But what exactly is the noindex? When do you use the nofollow? And how do you deploy the disallow?
In this article, I'll answer all those questions.
Before we begin: crawling vs. indexing
Within SEO, the terms crawling and indexing are incredibly important. And the difference between the two is perhaps even more important.
These are really basic elements of search engine optimization, so I'll explain them just to be sure.
Ps. About the difference between crawling and indexing, we have also included a podcats.
This is crawling
Crawling is the retrieval and tracing of websites and page on the Internet. New pages and new websites are added every second. Google has to value these, of course, but first Google has to know they exist at all.
Google does that through the Googlebot. That's Google's little spider that crawls the Web (literally and figuratively) looking for new URLs and domains.
The Googlebot tracks all links on a website to then assess which pages a website consists of.
So that's the crawling. In other words, taking all the URLs and websites.
This is indexing
Of course, if Google knows the existence of a page, the algorithm still has to read through it, go through the content and include it in its indexing/database.
Google will read through the page, so to speak, so it knows what your page is about.
This is because then the search engine will know which keyword your article best matches.
Crawl first, then index
If you have read the above explanation, then you know that Google must come along before you can be taken.
So your website must be crawled first and then indexed.
This is incredibly important to remember. Why? You're about to find out ;-).
What is noindex?
The noindex is an element found in your HTML (also called a meta tag) that indicates that your page (or website) should not be indexed.
With a noindex tag, you are telling Google that you do not want to be included in its indexing. Your page will then not be found in Google.
But that still means that the page is allowed to be crawled.
What is nofollow?
When you add rel="nofollow" to a link, you are basically telling Google, "I want you to not value this page, not crawl it and not index it.
Google used to always adhere to this, but for about a year now, Google sees it as advice. And that means Google can also ignore your advice.
The nofollow especially comes into play when you place links to other websites. After all, that's when you don't want to give away your value. Nofollow links are almost not used internally.
What is disallow?
A disallow should be placed in the robots.txt of your website. This indicates that Google should not crawl a page (or your entire website).
So this means that Google's spider (the Googlebot) does not come along.
But Google's spider can also enter in other ways. For example, through another website. And so your page can still be indexed.
Like this. Now that I've explained all three, you understand why the difference between crawling and indexing is so important.
What is the difference between the noindex, nofollow and disallow?
You may now be able to figure out the difference for yourself:
- A noindex ensures that your page is not included in indexing, but can still be crawled in the meantime.
- A nofollow can be included with a link, and with it you can advise Google not to crawl and index an external link.
- A disallow causes Google not to crawl a page, but the page can still be indexed
When do you use the noindex, the nofollow and the disallow?
Of course, there are many variables that determine which one you should use. I share with you a few situations that I have encountered many times (and thus are probably the most common):
- You set a thank you page to noindex because you don't want it to be indexed. You don't want someone to accidentally come to the page through Google.
- A test environment where you build a web site must be set to noindex and disallow. After all, you don't want anything or anyone to see this. Not even Google.
- You want your website's login environment set to disallow because you don't want Google to crawl it.
- You also set your WordPress shopping cart, checkout and account to disallow, because you don't want Google crawling those.
- External links (especially on pages that are important to you) should always be given a nofollow. After all, you don't want to lose value.
- External links to, say, a page that does matter to you don't want to include a nofollow.
How do you set the noindex, nofollow and disallow (with WordPress)?
Setting the noindex, nofollow and disallow are different for each CMS, so I cannot explain that in this article.
WordPress is the most widely used CMS, most of OMA 's clients have WordPress and if I show you how (easy) it is within WordPress, then I'm sure you can do it within your CMS as well.
Or you can just send your developer this article, and I'm sure he'll know how to do it.
Adding noindex on a page with WordPress
You can do this by setting the page to noindex within your SEO plugin (in our case Yoast).
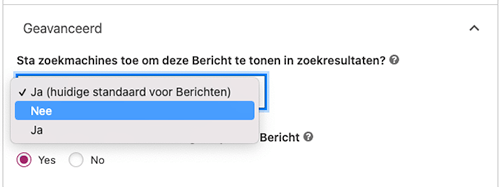
Adding noindex to your entire website with WordPress
You can do this by unchecking "search engine visibility" under Settings and Reading.

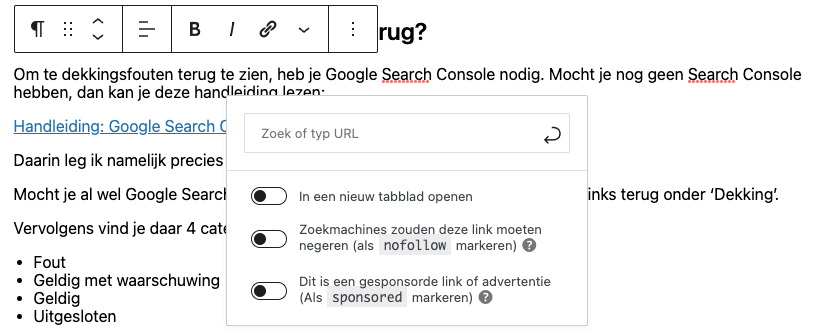
Adding nofollow to a link with WordPress
You add a nofollow by turning on the 'search engines should ignore this link - mark as nofollow' slider.
Add disallow within WordPress
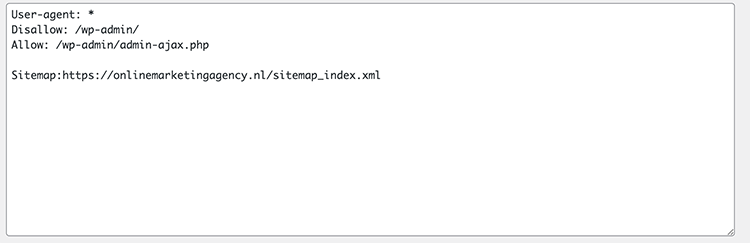
A disallow should be added within your robots.txt. The robots.txt is often generated by your SEO plugin. In our case, that means Yoast.
You can find the robotst.txt within Yoast under the Tools heading and then under File Editor.











Written by: Daniel Kuipers
Daniel is the founder of Online Marketing Agency. He constantly scours the Internet for the latest gadgets and tactics and blogs about them in understandable language. Well, sometimes.